Equations and Graphs
Overview: In this module we review
the essentials of interpreting and preparing graphical data and revisit the
graphical addition of vectors.
Skills:
- Determining slopes and y-intercepts from graphs
- Estimating specific data values from graphs
In the sciences, many times it is necessary to be able to interpret graphs
as well as be able to graph certain equations. Often data is available in a graphical format and you
must be able to extract the necessary information. Other times, it may be helpful to plot an equation in
order to fully understand a problem. However, graphing can be difficult for some students. The format in
this section is a little different. The first part will be simply showing what some special equations look
like in graphical form and the second part will be a series of questions to help you understand graphs better.
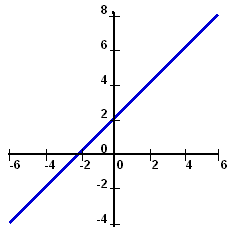 |
This graph shows a straight line and the corresponding equation is y
= mx + b. Y is the y value (distance along the y-axis, which is the vertical
axis) and x is the x value (the distance along the x-axis, which is the
horizontal axis). The slope of the line is m, which is also the rise/run
or the Dx/Dy. The
y-intercept of the line is b. This is the y value where the line crosses
the y-axis (when the x = 0). In the graph here, the slope is 1 and b is
+2. Notice that a line crosses each axis only once (at most).
|
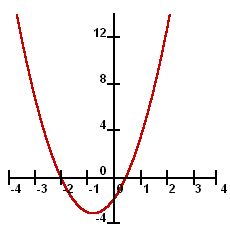 |
This graph represents a quadratic function, which is y = ax2
+ bx + c. The parameters a, b and c are constants. In this graph the actual
equation is y = 2x2 + 3x - 2. Notice that in this graph the
function crosses the y-axis once and the x-axis twice. This has to do
with the fact that x is squared in the equation and y is not. The function
crosses the axis (up to) the same number of times as the power of that
value. In this graph x is squared so the line crosses the x-axis up to
two times.
|
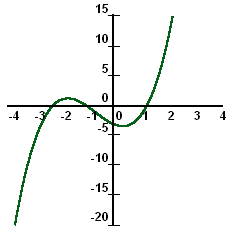 |
This graph shows a cubic equation, which is expressed mathematically as y =
ax3 + bx2 + cx + d. For this particular function,
y = x3 + 2 x2 - 2 x - 3. Because x is raised to
the third power, the function crosses the x-axis 3 times. It crosses the
y-axis only once however.
|
 |
This is a log plot. Notice that the x-axis is quite different than in the other
graphs. In this graph, if we look at the y-axis we see that the distance
from 1 to 10 is the same as that from 10 to 100. But we know that the
span from 10 to 100 represents a much larger range of x-values than that
from 1 to 10. This is a property of a log plot. Be sure to look at the
axis on a log plot (as well as all graphs) in order to understand exactly
what the graph is trying to show.
|
In order to answer the following questions, you need to have a good understanding of the preceding subjects
in the tutorial.
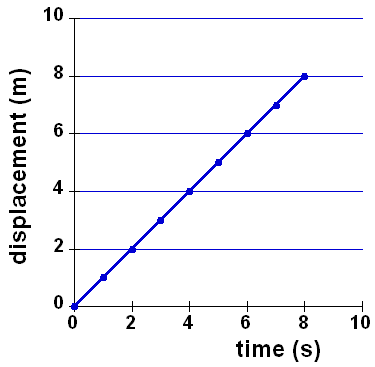
| 1. |
A particle's movement is plotted on the right. Use the information to
answer the following questions.
- a. How far has the particle moved at 4 s? Answer
- b. How long does it take for the particle to move 6 m?
Answer
- c. What is the particle's velocity? Answer
|
 |
| 2. |
Another particle moves on a trajectory described in the plot on the right.
- a. How long does it take for the particle to move 16 m from its starting position? Answer
- b. How far does the particle travel in the first 5 s? Answer
- c. Is the particle accelerating? Answer
|
 |
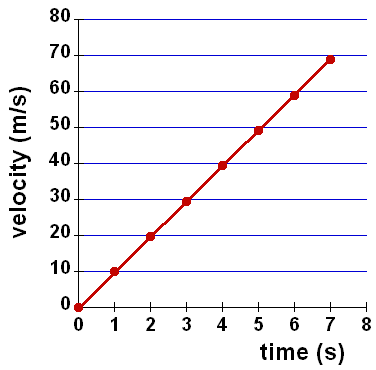
| 3. |
A ball is dropped from the top of a building and its fall is plotted in the
graph to the right.
- a. Is the ball accelerating? Answer
- b. What is the velocity at 1 s? Answer
- c. How long does it take for the ball to reach a velocity of 49 m/s? Answer
- d. What is happening to the ball's potential energy as it falls? Answer
|
 |
| 4. |
- a. How many times would the following function cross the y-axis?
5y6 + 7y3 + 5x4 – 2x2
= 0?
Answer
- b. For the same equation, how many times will it cross the x-axis? Answer
|
|
Summary
In this module we have reviewed the essential skills necessary for interpreting
data presented in a graphical format. Interpretation of graphical data is a routine
skill used by the practicing scientists, physicians, and engineers. You will develop
these skills further in your specific discipline at Washington Univeristy.
Return to the Chemistry Subject Index